Background
On September 28, 2018 significant revisions to the Global Industry Classification Standard (GICS) structure went into effect. GICS is the global industry classification standard jointly developed by MSCI and Standard & Poor's. It is a four-tiered, hierarchical classification system that categorizes companies into 11 sectors, 24 industry groups, 69 industries and 158 sub-industries. The final classification results in an 8-digit GICS code.
The recent changes reflect the ongoing evolution in the way companies interact with consumers. Many companies have contributed to this evolution through mergers and acquisitions whereby they now offer solutions that address multiple consumer needs related to communicating and accessing digital content.
Summary of changes
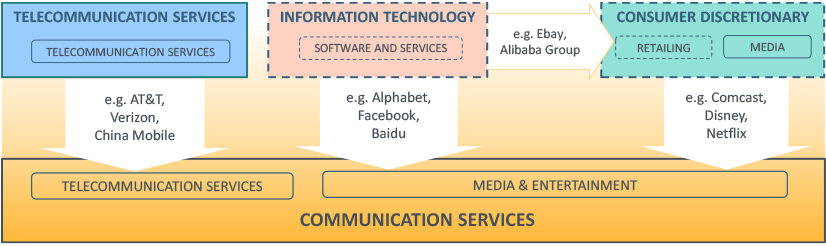
The Telecommunication Services GICS sector is being expanded and will be renamed as "Communication Services." It will include all of the existing telecommunication companies, as well as certain companies that have been identified from: 1) the Media Industry group (Consumer Discretionary sector); 2) the Internet & Direct Marketing Retail sub-industry (Retailing industry group, Consumer Discretionary sector); and, 3) the Information Technology sector.
The details of the proposed changes are as follows:
- The "Telecommunication Services" sector will be expanded and renamed the "Communication Services" sector;
- Media companies will transfer from the "Consumer Discretionary" sector to the "Communication Services" sector;
- Internet services companies will transfer from the "Information Technology" sector to the "Communication Services" sector; and e-commerce companies will transfer from the "Information Technology" sector to the "Consumer Discretionary" sector.
Issues to consider
The major proxy advisory firms, particularly Institutional Shareholder Services, Inc. (ISS), in their analyses and vote recommendations use the GICS structure to formulate peer groups to benchmark a company's information. Although we are unable to predict how these revisions will change ISS's analyses, we anticipate that the following areas will be affected:
- ISS develops the relevant peer group constituents for issuers twice per year in January and July. Consequently, ISS has already determined peer groups for issuers until it revisits the criteria in the December 2018 / January 2019 timeframe. At that time, there may be some material changes to how the peer groups are organized.
- ISS depends on the GICS structure to organize peer groups that are used to inform its voting recommendations on compensation-related proposals, such as "say-on-pay" and equity-based incentive plan proposals. The reorganization of some parts of the GICS structure will likely result in changes to the constituents in the peer groups. This could affect ISS's assessment of a subject company when comparing it against a revised peer group.
- As a result, the relative pay for performance alignment under ISS's quantitative analysis can move a company from a low to an elevated concern level, or vice versa, affecting the final vote recommendation under the say on pay proposal.
- Under ISS's Equity Plan Scorecard approach for equity plan proposals, the change in GICS group would likely affect the Shareholder Value Transfer (SVT) and Burn Rate analyses where peer groups are used to benchmark a company's equity cost and share usage.
- ISS reports show comparisons of a company's Total Shareholder Return (TSR) against that of a 4-digit GICS group. ISS also considers this comparative TSR performance as a factor in its analysis of certain proposals which may therefore get impacted. Independent chair shareholder proposals and director performance evaluation under Election of directors are two such examples.
Impact on issuers:
We recommend that companies monitor the above mentioned impact of GICS group changes. It would be especially important for those companies that are marginally above or below median in their relative performance within their comparator GICS group.